JSF is server side UI component framework. JSF contains API for
representing UI component and managing their interface state, handling event,
server side validation and data conversion, defining page navigation supporting
internationalization and accessibility and providing extensibility for all
these features.
Backing
Bean:-
Backing Bean is referenced by a form, it is defined only in
request scope.
Managed
Bean:-
Managed Bean is Backing Bean that has been registered with JSF (faces-config.xml)
and it automatically created by JSF.
Managed Bean scope is request, session and application.
Managed Bean declaration:-
<managed-bean>
<managed-bean-name>hello</managed-bean-name>
<managed-bean-class>com.mk.test.Hello</managed-bean-class>
<managed-bean-scope>session</managed-bean-scope>
</managed-bean>
Or Using @ManagedBean annotation with @SessionScoped
Navigation rule:-
<navigation-rule>
<from-view-id>login.xhtml</from-view-id>
<navigation-case>
<from-action>#{Controller.page1}</from-action>
<from-outcome>success</from-outcome>
<to-view-id>home.xhtml</to-view-id>
</navigation-case>
<navigation-case>
<from-action>#{Controller.page1}</from-action>
<from-outcome>failure</from-outcome>
<to-view-id>
login.xhtml</to-view-id>
</navigation-case>
</navigation-rule>
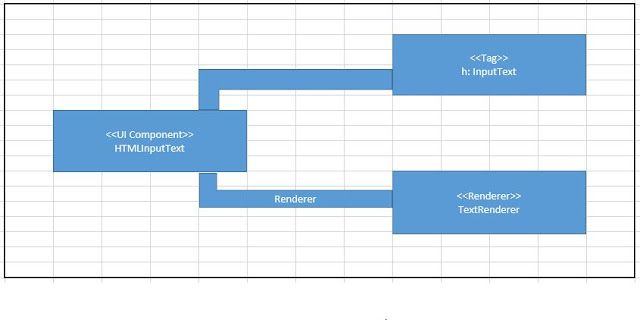
JSF Custom component:-
JSF Component is made up of three classes that works
closely together.
-
Renderer:
- Creates client side representation of the component, it takes any input from
client and convert in component understandable form.
-
UI
Component: - This class is responsible for data and behavior of
the component on the server side.
-
JSP
Custom Action: - It allows configuration of component in JSP
pages.

very usefull in full details thanks
ReplyDelete